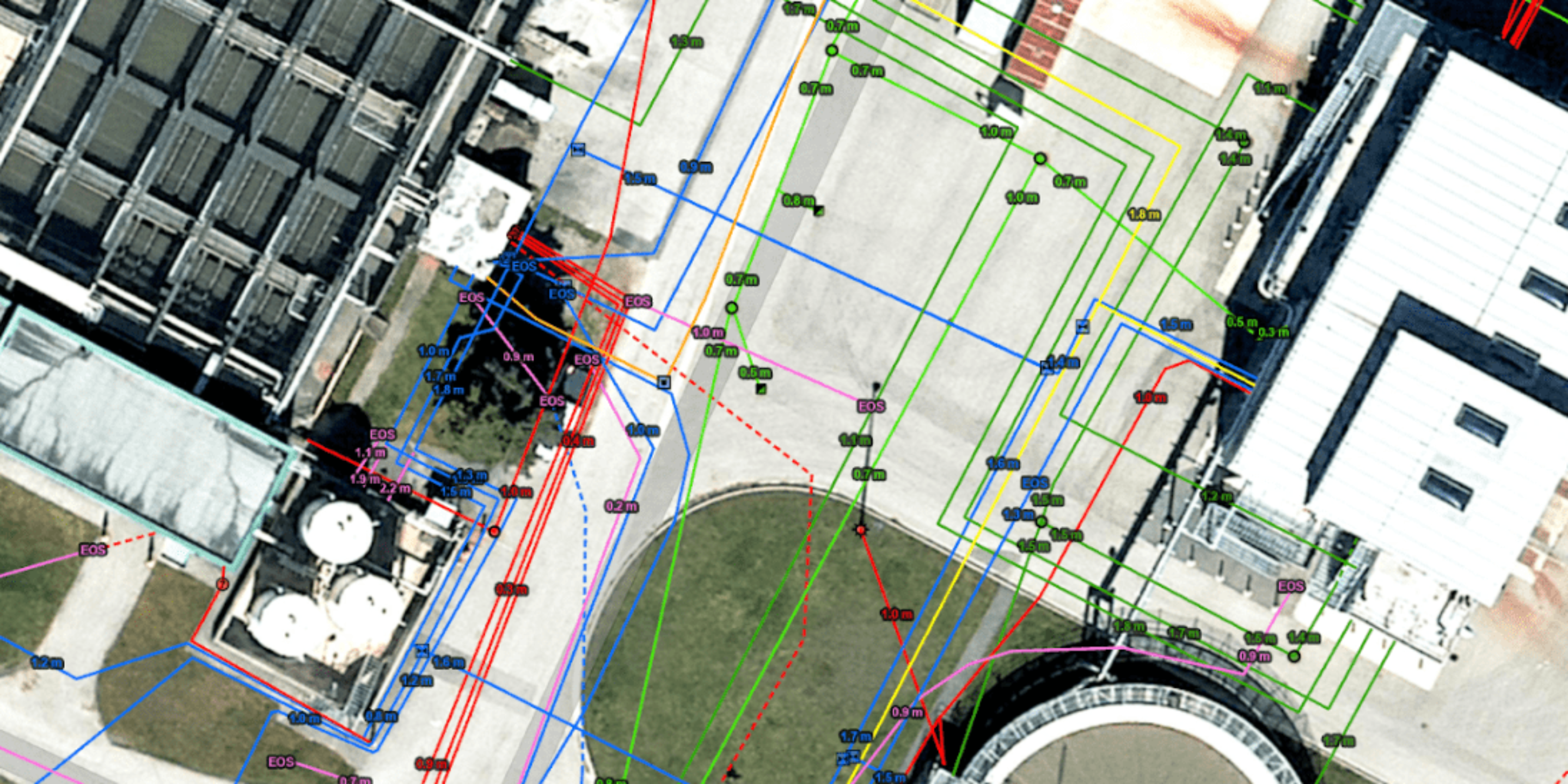
Using cutting-edge GIS technology, we create base maps of small cities and municipalities.
These allow municipal planners and civil engineers to better plan their underground utility systems and manage them effectively when repairs or replacements are required.

GIS (Geographic Information System) is a system of hardware, software, and data for capturing, storing, analyzing, managing, and displaying all forms of geographically referenced information.
A skilled GIS specialist can create interactive maps, 3D scenes, and other visualizations that can be used to analyze and understand relationships, patterns, and trends in the data. It can also be used to inform decisions and solve problems related to geography and the environment.
GeoScan applies it in a variety of fields, such as urban planning, natural resource management, transportation, and business to:
- Capture, store, and manage spatial data, such as points, lines, and polygons
- Analyze and manipulate that data using various tools and techniques
- Create maps, 3D models and other visualizations to display the data
Applications and Benefits of GIS Utility Mapping
GIS utility mapping is the process of creating and maintaining digital maps that show the location and attributes of various utility infrastructure such as water, gas, and electrical lines. This information is used by utility companies, municipalities, and natural resources management companies to plan and manage their operations, as well as to respond to emergencies and outages.
By utilizing GIS data and simulation technology, municipalities can configure their utility network, anticipate potential issues such as impassable areas, and incorporate this information into the initial pre-design and planning stages. With a base map of utilities, large-scale projects such as installing and updating hydro corridors, tunnels, water mains and wastewater services, natural gas pipelines, and telecommunications lines can be efficiently managed.
- Improved efficiency: GIS technology allows utility companies and municipalities to easily access, update, and share information about their infrastructure, which can improve the efficiency of their operations and decision making.
- Better asset management: Offers detailed information about the location, condition, and age of utility assets, which can help with planning for maintenance, replacement, and expansion.
- Enhanced emergency response: Provides critical information to emergency responders during an emergency, such as the location of gas lines or electrical substations.
- Better customer service: Provides customers with information about outages and estimated repair times, as well as to identify and resolve issues with individual service connections.
- Increased safety: Identifies potential safety hazards, such as gas leaks or electrical substations located near schools or residential areas.
- Cost savings: Reduces costs by identifying and resolving issues before they become major problems, and by reducing the need for field visits.


